|
||
|
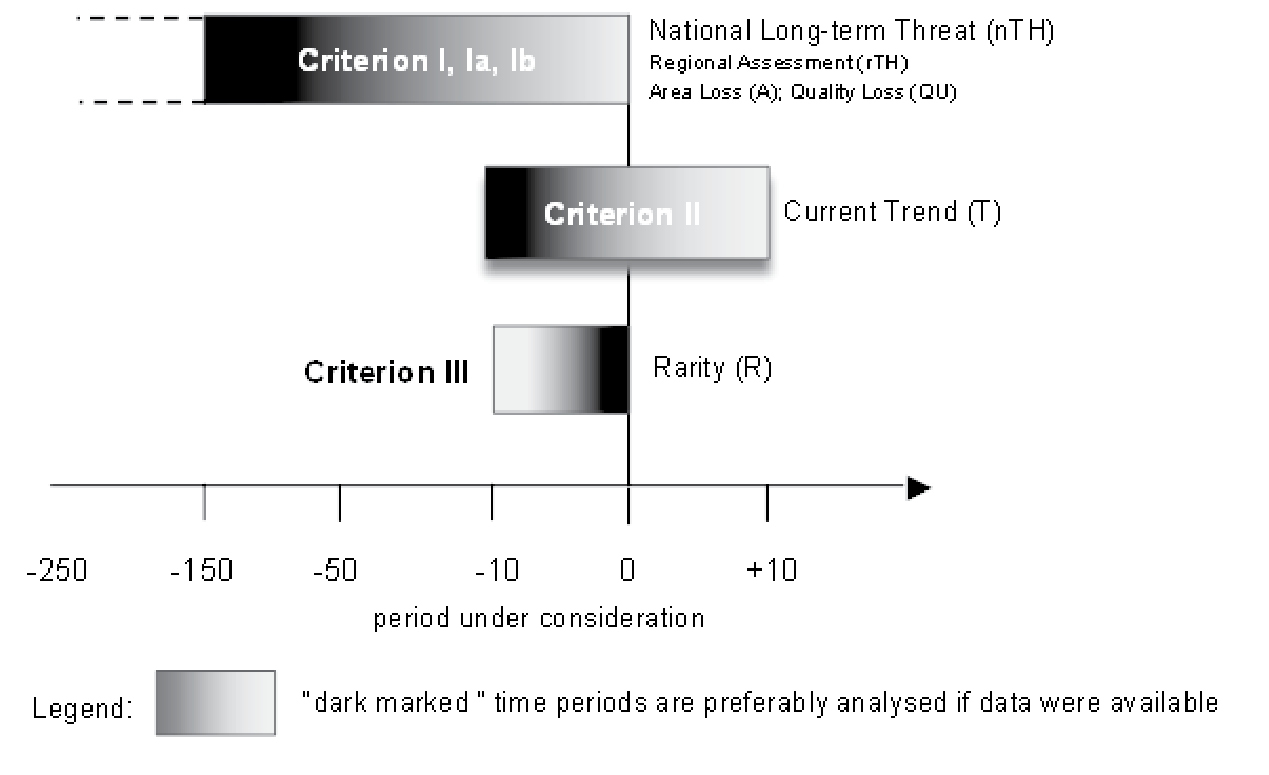
Time frames of the three red listing criteria of the German Red List (Finck et al. 2017). For the long-term evaluation (nTH), mainly anthropogenic spatial (sub criterion AL) and qualitative (sub criterion QUL) changes over the last 50–150 years (sliding time frame) are assessed for the major regional landscape units. The estimation of the ‘Current Trend’ (T) is based on development over the last ten years and a forecast for the near future (maximum ten years). A higher risk of loss is basically assumed for habitat types which are ‘Extremely Rare’ at present (R). The latter includes both ‘natural’ rarity as well as rarity as a result of human impact. |